Low-code platforms are transforming how IT and business teams work together by simplifying app development and reducing bottlenecks. Here's a quick summary of how they help:
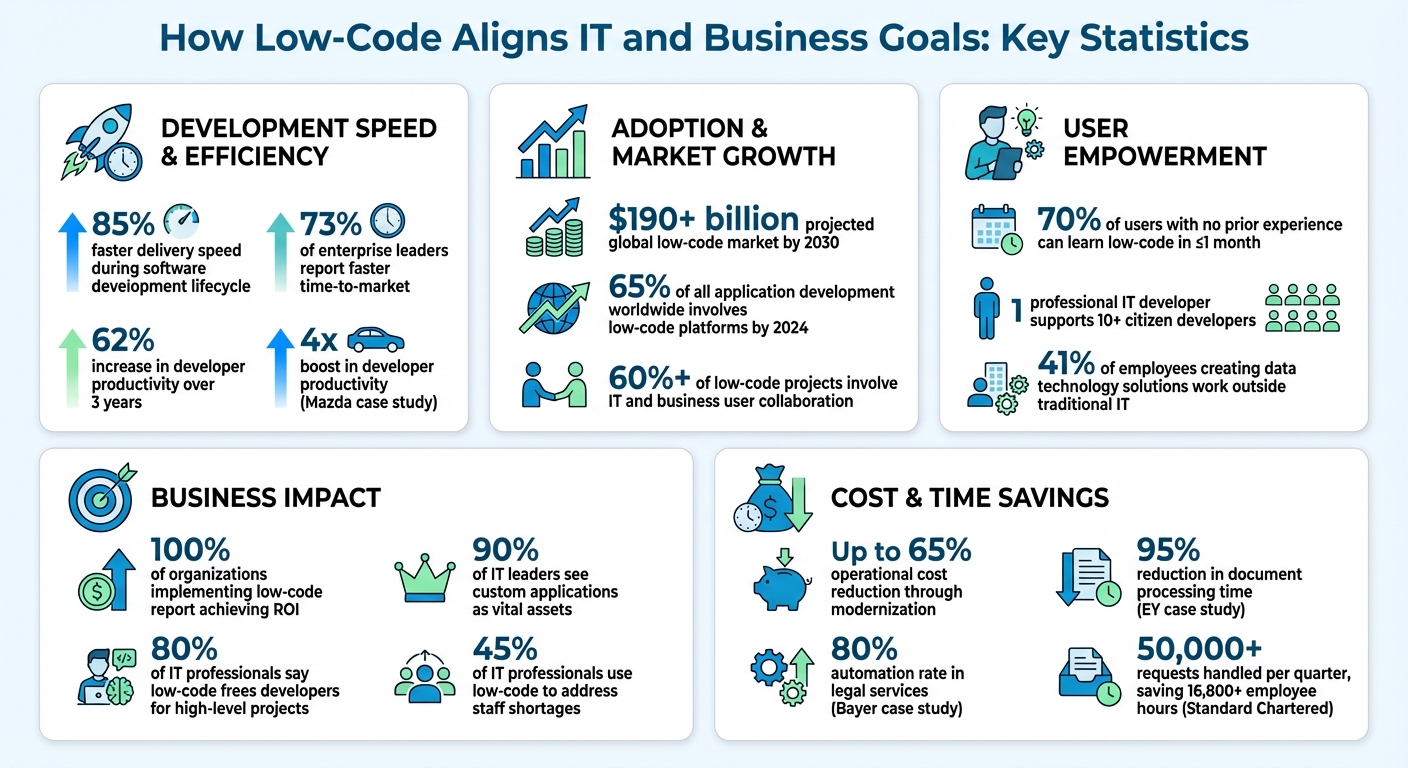
- Faster Development: Low-code speeds up software delivery by up to 85%, cutting months-long timelines into days.
- Collaboration: Visual interfaces allow business users and IT to co-create solutions, reducing miscommunication.
- Empowering Non-Technical Users: Tools like drag-and-drop interfaces enable non-technical staff to build apps, easing IT backlogs.
- Cost Efficiency: Organizations save time and resources by modernizing legacy systems without complete overhauls.
- Governance: Centralized and decentralized governance models ensure low-code security while allowing flexibility.
With the global low-code market projected to surpass $190 billion by 2030, it’s clear that these platforms are reshaping how businesses innovate and stay competitive.
Key Takeaway: Low-code empowers businesses to create faster, more collaborative, and cost-effective solutions while aligning IT and business priorities.
Low-Code Platform Benefits: Key Statistics on Speed, Collaboration, and ROI
1758: MuleSoft - The IT and Business Alignment Barometer Report
sbb-itb-33eb356
How Low Code Breaks Down Organizational Silos
Low code platforms are reshaping the way organizations bridge the gap between IT and business teams. Traditionally, IT spoke in technical jargon like code and architecture, while business teams focused on workflows and customer needs. Low code changes this by creating a shared space where both groups can collaborate effectively. This shift empowers non-technical users and encourages real-time teamwork across departments.
Giving Non-Technical Users Development Capabilities
Low code platforms simplify development by replacing complex coding with user-friendly tools like free low code platforms with drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built templates. This makes it possible for non-technical users to create their own solutions. In fact, research shows that 70% of users with no prior experience can learn to use low-code platforms in a month or less. Imagine HR managers, finance analysts, or supply chain coordinators building their own apps without waiting for IT to clear a backlog.
"We expanded our capabilities beyond the walls of our IT department. Our marketing department used low-code platforms to build ad tracking applications, while our finance and operations teams transformed spreadsheets into online databases and managed workflows." – Isaac Sacolick, President of StarCIO
This approach, often called citizen development, allows subject-matter experts to design tools tailored to their needs. By 2024, Gartner estimated that over 65% of all application development worldwide would involve low-code platforms, with one professional IT developer supporting 10 or more citizen developers. This means organizations can achieve much more without adding technical staff, as everyday users take on tasks traditionally handled by IT.
When non-technical users have the tools to create their own solutions, it naturally fosters smoother communication and collaboration across departments.
Better Communication Across Departments
Low code platforms bring IT and business teams together from the very beginning. By using real-time visual interfaces, they eliminate the common issue of "misinterpreted requirements", where business needs get lost in translation when converted into technical specs. Instead of submitting requests and hoping for the best, teams collaborate side by side on the same platform.
Features like shared app repositories, sandbox environments for testing, and built-in approval workflows make this collaboration seamless. Today, IT professionals and business users collaborate on more than 60% of low-code development projects. This isn’t just about coordination - it’s genuine co-creation. Business teams take ownership of their solutions, while IT ensures governance and technical support.
The impact is clear. Standard Chartered Bank used low code to build a platform that handles over 50,000 requests per quarter, saving more than 16,800 employee hours. Bayer achieved an automation rate of up to 80% in its legal shared services function. These results are possible because the people who understand the work best are directly involved in creating the tools they need.
Faster Development and Iterative Changes
Low code transforms how teams collaborate and deliver solutions, speeding up development and response times. In fast-moving markets, IT and business teams must adapt quickly to shifts in customer needs. By replacing manual coding with visual tools and pre-built components, proprietary low code platforms cut down on lengthy development timelines. This isn't just about saving time - it's about redefining how organizations deliver results.
Shorter Time-to-Market
Traditional software development often stretches over months or even years. Low code changes the game with drag-and-drop interfaces, ready-to-use templates, and functional modules that eliminate the need to start from scratch. The results speak for themselves: low code can boost delivery speed by up to 85% during the software development lifecycle, and 73% of enterprise leaders report faster time-to-market.
Take this example: In July 2019, a global logistics company used low code to shrink its invoicing turnaround from 13 weeks to just 2 weeks, speeding up revenue collection by millions of dollars. Around the same time, a clinical research support provider cut its data management workload by 80% using low code. More recently, in February 2026, Jellyvision tripled the speed of its lead routing processes through low code workflow automation.
"Low-code platforms can dramatically speed the creation of sophisticated enterprise-class applications that incorporate complex business logic, automate workflow and case management activities, integrate with existing information systems, and enable a slick user experience." – KPMG
This ability to deploy solutions quickly sets the stage for ongoing improvements and adjustments.
Real-Time Updates and Adjustments
Low code doesn’t just speed up the initial launch - it also supports continuous updates and refinements. Instead of waiting months for a polished final product, teams can release a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and improve it based on real-world feedback. This modular approach, often referred to as the "composable enterprise" model, allows for flexible, on-the-fly adjustments to meet evolving market demands.
Because low code enables simultaneous design, testing, and deployment, business teams can see changes in real time, test new features instantly, and offer feedback without delays. This streamlined feedback loop is why 74% of technical leaders believe low code accelerates innovation cycles. With IT and business teams working together on the same platform, updates that once took weeks can now happen in days - or even hours.
Making Application Development Accessible to Business Teams
Low code is changing the way businesses approach application development. By allowing business teams to directly create and adjust applications, it removes the delays often associated with IT involvement. This matters because 90% of organizations see custom software as a key driver of their strategy, yet many still struggle to deliver solutions quickly enough. When business users take the lead, they ensure their needs are met without miscommunication or delays.
Customizing Solutions to Match Business Requirements
Who knows a workflow better than the people who use it every day? Low code platforms make it easy for subject matter experts to turn their knowledge into functional applications using drag-and-drop tools and pre-built templates. This hands-on approach eliminates the risk of misinterpretation and ensures the final product aligns perfectly with their needs.
Take EY's Global Finance team, for example. In 2021, they used Microsoft Power Platform to create "Power Post", an application that automated their General Ledger posting process. The result? A 95% reduction in document processing time, 30% lower costs, and the elimination of manual workflows involving emails and Excel. Similarly, PwC developed its "Cyber Technology Rationalizer" in just six weeks, cutting costs by 85% and saving 30% of the time compared to traditional methods.
"Technical requirements may get lost in translation... This heightens the possibility of receiving an application from IT that does not meet the exact needs of the department, even after waiting a long time for the finished product." – Isaac Sacolick, President, StarCIO
Low code platforms also come with templates for common processes like CRM, HR onboarding, and lead routing. Business teams can tweak these templates to fit their specific needs, ensuring applications are tailored from the start. This not only leads to better solutions but also allows IT teams to focus on bigger challenges.
Reducing IT Backlogs
IT departments are often stretched thin, with many managers reporting that over 40% of IT requests are delayed due to competing priorities. Low code helps ease this burden by shifting simpler tasks - like lead routing, employee onboarding, or IT ticketing - to business teams. This frees IT professionals to focus on high-level strategic work, such as governance and security.
It’s no surprise that 45% of IT professionals turned to low code to address staff shortages. These tools have been shown to increase developer efficiency by 62% over three years. Additionally, 81% of CXOs and directors have introduced training programs for "citizen developers", enabling employees to use their expertise to create solutions.
| Feature | Low-Code vs Traditional Development | Low-Code Business-Led Development |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Months-long backlog | Hours or days |
| Requirement Accuracy | Risk of miscommunication | Built by subject matter experts |
| IT Focus | Spread thin across all requests | Focused on critical tasks |
| Maintenance | IT-dependent updates | Self-service adjustments |
Low code lets business teams take charge of their own development needs, especially given that the average department now relies on 40–60+ applications. IT still plays a crucial role in ensuring security and compliance, but the ability of business teams to handle their own tools means solutions can be delivered faster and more efficiently, right when they’re needed.
Maintaining Governance and Security in Low Code Implementations
To empower business teams while keeping operations secure, organizations need solid governance frameworks that act as guardrails. These frameworks cover key areas like platform access, lifecycle policies, compliance standards, versioning, and security controls. Their purpose? To prevent risks like "shadow IT" and data leaks - all without slowing down development.
"Low-code governance is the discipline of managing and overseeing low-code app development. It covers everything from platform access, lifecycle policies, and compliance to versioning and security controls." – Nutrient
The first step in governance is setting clear boundaries: Who can build? What can they build? Who reviews and approves their work? From there, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies come into play, regulating which connectors can be used and where sensitive data can flow. Security trimming ensures that users only access the data and functions they’re authorized for. Even with automation, professional code reviews remain critical for catching vulnerabilities. These principles help organizations strike the right balance between agility and security.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Governance Models
When it comes to governance, organizations usually take one of two approaches. Centralized governance puts IT in charge - often through a Center of Excellence (CoE) - to enforce standardization, security, and compliance across the board. On the other hand, decentralized governance gives more freedom to business units and citizen developers, allowing them to create solutions independently within IT-defined boundaries. While this approach offers speed, it also increases the risk of shadow IT and data silos.
A fusion model often delivers the best results by combining centralized IT oversight with decentralized execution. IT defines the rules, maintains the infrastructure, and monitors compliance, while business teams build applications within those guidelines. This approach ensures both security and speed, a necessity as 41% of employees who create data technology solutions now work outside traditional IT departments.
| Feature | Centralized Governance | Decentralized Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Driver | IT Department / CoE | Business Units / Citizen Developers |
| Security Risk | Low (Standardized controls) | High (Potential for shadow IT) |
| Agility | Moderate (May have bottlenecks) | High (Rapid development) |
| Scalability | Sustainable (Managed growth) | Rapid (High volume of applications) |
| Compliance | High (Strict adherence) | Variable (Depends on user training) |
This fusion of centralized control and decentralized creativity keeps IT and business teams aligned while staying secure.
Role-Based Access Controls and Compliance
Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) are a cornerstone of secure low-code development. RBAC allows organizations to fine-tune permissions at multiple levels - workspaces, applications, data sources, individual pages, or even specific rows and fields. The concept is straightforward: users only get the access they genuinely need.
RBAC also separates roles into "Build" (for designing UI and logic) and "Operate" (for running processes and viewing logs), preventing unauthorized changes in production environments. Many low-code platforms integrate with identity providers like Microsoft Entra ID, Okta, and Google Workspace, ensuring access is quickly revoked when employees leave. Additionally, these platforms support environment isolation through sandboxes and multi-environment setups (Development, Staging, Production), restricting who can promote applications to live environments.
"Governance is the bridge between agility and control. For pro developers, governance ensures that low-code does not lead to application sprawl, shadow IT, or security vulnerabilities." – Javeria Husain, Content Writer, Quickbase
Best practices include assigning permissions to groups rather than individuals, making new applications private by default, and keeping audit trails for every permission change. For added security, conditional access policies can block access from untrusted networks or devices. These measures are crucial for compliance with regulations like SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA, especially in industries like healthcare and finance.
Modernizing Legacy Systems with Low Code
Low-code platforms do more than just streamline development - they breathe new life into outdated legacy systems while fostering collaboration between IT and business teams. On average, maintaining a legacy system costs enterprises around $40,000 annually per system, without adding much value. Additionally, 59% of applications struggle with issues like outdated technology and scalability limitations. The "rip and replace" approach, while tempting, is risky - 79% of such projects fail, often taking 16 months and costing $1.5 million. Low-code platforms offer a safer alternative by acting as a bridge, enabling gradual modernization without disrupting daily operations. This approach ensures smoother IT-business alignment, allowing for continuous improvements.
Integration Layers for Legacy Systems
Low-code platforms excel at modernizing legacy systems by serving as an integration layer. Through APIs and connectors, they wrap outdated functionality in modern interfaces, allowing older systems to remain operational while adding new features. Instead of rewriting code from scratch, organizations can expose existing business logic via APIs that low-code applications use to create sleek, modern front ends, all while keeping the legacy backend intact.
"Low-code platforms offer a flexible approach to increase modernization speed, packaging up existing business logic in the legacy application via APIs, and consuming them in modern, performant, and secure front ends." – Vikram Srivats, Chief Commercial Officer, WaveMaker
For instance, Mazda Motor Corporation faced the daunting task of migrating 500 legacy systems to a modern Java framework by 2026. Using low-code, they achieved a 4x boost in developer productivity and slashed deployment cycles by 70%, cutting training time from months to just two weeks. Similarly, Maeda Corporation transitioned 1,000 legacy Lotus Notes databases into over 200 modern web applications in two years. This resulted in a 5x improvement in user satisfaction, all without any downtime during the migration.
Step-by-Step Modernization Strategies
To complement the integration approach, a phased modernization strategy helps minimize risks. Starting small is key - organizations should focus on less critical applications or peripheral functions first rather than diving into core systems. This is often referred to as the "strangler fig" pattern, where new systems are built around the edges of legacy applications, gradually replacing components until the old system can be retired.
A great example of this is the UK Crown Prosecution Service, which embraced incremental modernization over six years. They expanded their citizen developer team from 2 to 16 members and developed 30+ applications to replace legacy systems, with an average development time of just four months per application. This step-by-step approach allowed them to build internal expertise while proving the concept before tackling more complex systems.
This gradual modernization strategy can result in operational cost reductions of up to 65%. It’s like renovating a building one floor at a time while people still live in it - avoiding the chaos and risk of a complete teardown.
Conclusion: Low Code as a Driver for IT-Business Alignment
Low-code platforms are proving to be a powerful link between IT teams and business goals. By enabling citizen developers - non-technical employees in areas like marketing, finance, and operations - these platforms help close the gap between business needs and technical execution.
Research highlights their impact: every organization implementing low-code has reported achieving ROI, and 90% of IT leaders now see custom applications as vital assets. With 81% of companies constrained by limited budgets for custom development, low-code has shifted from being a convenience to becoming a financial lifeline. Businesses leveraging low-code spend more time driving innovation rather than maintaining outdated systems, and 80% of IT professionals say these tools free up developers to focus on high-level projects.
"Low-code workflow automation bridges the gap between IT teams and business users by giving citizen developers the power to set up integrations and create powerful automated workflows without tapping development resources." – Tray.ai
The benefits extend beyond efficiency. Low-code platforms support the transition to a composable enterprise model, where modular, adaptable software allows rapid responses to market shifts. This adaptability is critical in today’s landscape, where departments often juggle 40–60+ different applications that must integrate seamlessly.
With the global low-code market expected to surpass $190 billion by 2030, adopting these platforms positions organizations to innovate quickly while maintaining strong governance and security. For those ready to explore their options, the Low Code Platforms Directory (https://lowcodeplatforms.org) offers tailored filters for features like AI, automation, and CRM, helping businesses find the perfect fit to achieve unified success.
FAQs
How do we start low-code without creating shadow IT?
To kick off low-code development while avoiding shadow IT, it's crucial to bring both business and IT teams together from the start. This ensures proper governance and alignment. Set up clear guidelines and implement structured citizen development programs backed by IT to manage adoption effectively. By encouraging transparency, teamwork, and providing training, organizations can securely integrate low-code platforms into enterprise systems. This approach supports innovation, keeps compliance in check, and ensures IT and business goals stay aligned.
What apps should we build first with low code?
When diving into low-code development, it’s smart to begin with applications that solve pressing issues and provide tangible results quickly. Examples include custom CRM systems, process automation tools, or apps that turn complex spreadsheets into web-based solutions. These types of projects simplify workflows and boost overall efficiency.
Another great focus is on apps that drive digital transformation, such as those automating repetitive tasks or integrating disconnected systems. These "quick win" projects not only showcase the value of low-code platforms but also help build momentum for wider adoption across your organization.
How do low-code apps connect to legacy systems safely?
Low-code applications make it possible to connect securely with legacy systems through APIs, facilitating data exchange without the need to modify existing infrastructure. To ensure security, middleware and secure gateways often play a role by enabling encryption, authentication, and regulating data transfers. Additionally, strong governance practices - like role-based access controls and continuous monitoring - add another layer of protection. These methods ensure safe integration, preserve system stability, and help support modernization goals.


